fefds
fefds
fefds
fefds
fefds
fefds
fefds







Module 7 (Field & Waves)

Field & Waves introduces students to electro- and magnetostatics. This knowledge is used to model and design an antenna. Students will also visit CERN in Géneve.
Subjects Module 7
Complex engineering problems – like describing a wing’s airflow profile, or an electrical spool’s magnetic field – require a mathematical description that employs vectors, a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction in 3 dimensional space. In this module you will apply vector mathematics in the field of electromagnetism. The behaviour of electric and magnetic fields and their interaction is given by the so-called Maxwell equations. Just four differential equations that describe a wealth of phenomena ranging from big magnets used for medical imaging to the behaviour of light (which is an electromagnetic phenomena) to the interaction between electrons and protons. In a Problem Based Learning style you will solve and discuss successive problems with a small group of students to get insight first in electrostatics, followed by magnetostatics. With magnetostatics you are already able to understand the design of electromagnets, magnetic fields created by a constant current.
Electrostatics and magnetostatics are combined in the field of electrodynamics, the mutual interaction of electric and magnetic fields. This forms the basis to understand optical effects and wireless communication. This knowledge will have to be used in the project team for the design and realization of an antenna that works as well as possible within the 100 MHz range.
To support the antenna design process the Finite Element Method is introduced. The Finite Element method is used in many engineering areas to evaluate a system described by (partial) differential equations such as fluid motion, thermal behaviour, mechanical stress and bending as well as electromagnetic phenomena. In many engineering problems it is actually a combination of these effects that play a role, for example the cooling of a mechanical structure to prevent thermal expansion with the flow of a cooling fluid. Working with a Finite Element method is not just asking the computer for an answer, as an answer it will give. Therefore this technique can only be used with a proper set-up of the problem and the validation of the results.
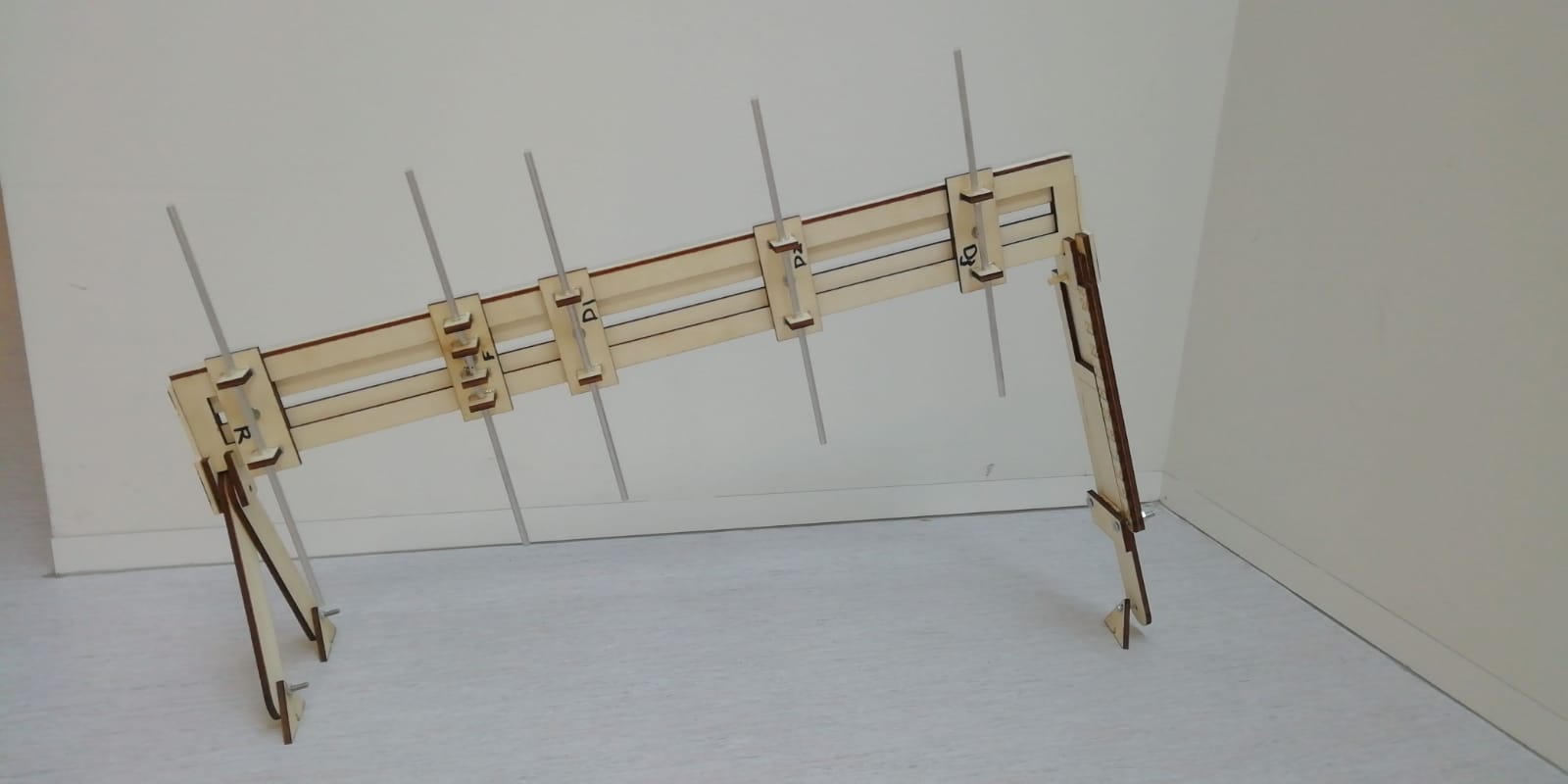
Antenna
An example of a build Yagi Uda antenna
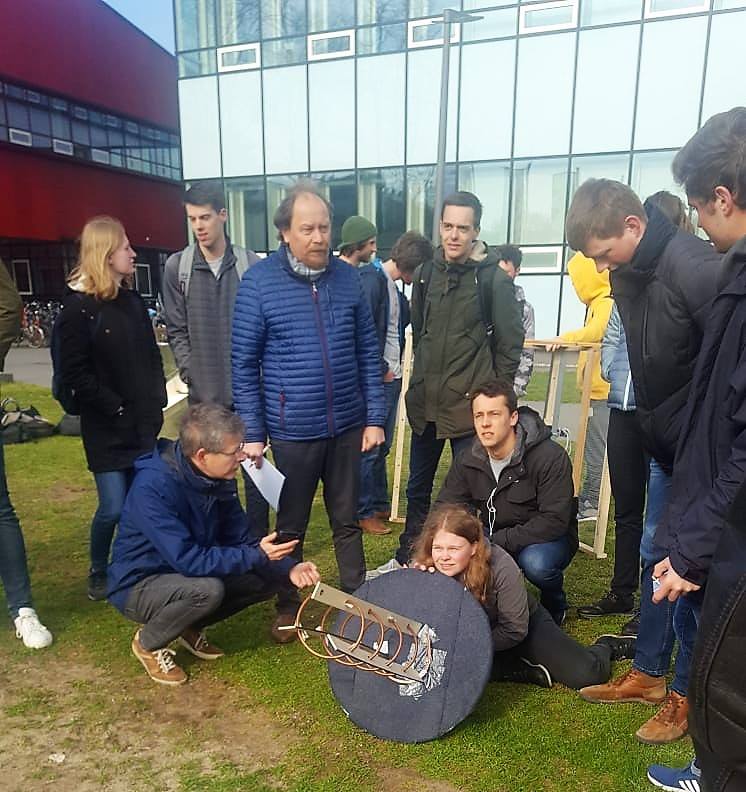

Antenna competition
On the final day of the antenna project you are going to test the strength of the signal from one building to the other
CERN trip
In the last few years one week of this module is spent on an excursion to CERN to see large magnets of various designs at work. During this visit several problems associated with particle beam dynamics and magnet design and realization are made. Above all this trip provides insight in this international renown institute.
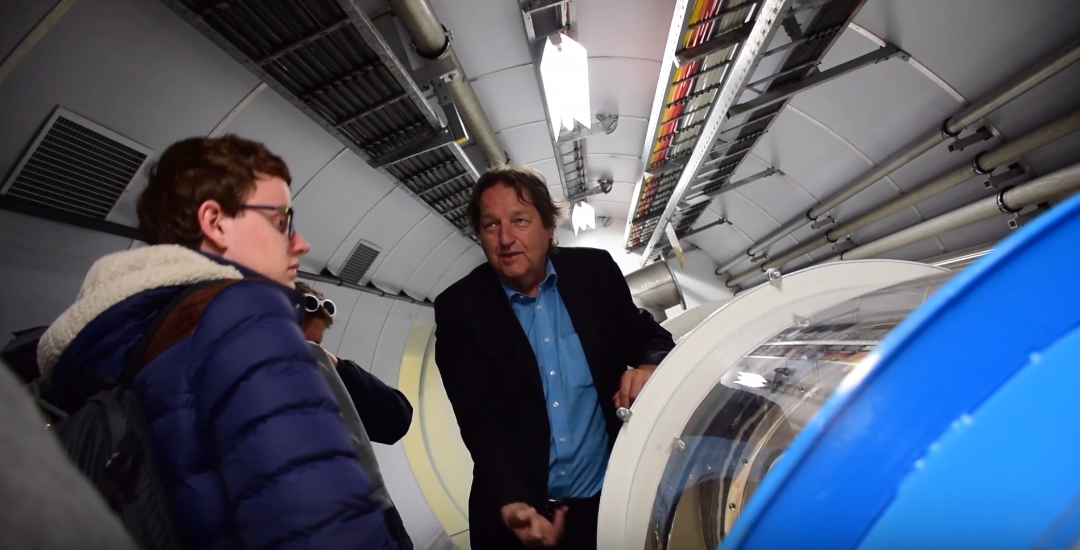

Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
You can see the LHC depending on the state of it